Next-Gen Form Filling with Gemini 1.5 Pro
Published:
Filling out forms can be boring and time-consuming. This often leads to user frustration and incomplete submissions. However, conversational AI, like the Gemini 1.5 Pro language model, is changing how we interact with forms.
Using Gemini 1.5 Pro with LangChain make form filling easy and engaging. Instead of dealing with complicated forms, users can simply provide information through a chat interface.
In this tutorial, I’ll show you how to leverage Gemini 1.5 Pro to enhance your user experience by replacing the traditional form method with a user-friendly form-filling experience. Using conversational AI can greatly improve user satisfaction and make data collection more efficient. Let’s see how Gemini 1.5 Pro can change the way your users interact with forms.
Prerequisites
Before starting, ensure you have the necessary libraries installed. Run the following command to install the required packages:
!pip -q install langchain langchain_community langchain_google_genai gradio > /dev/null 2>&1
Step 1: Import Libraries, Set the API Key, and Initialize Gemini 1.5 Pro
First, we’ll import the necessary libraries and configure the environment.
# Import Libraries
import os
import getpass
import gradio as gr
import random
from typing import Optional, List
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import JsonOutputParser
from langchain_google_genai import ChatGoogleGenerativeAI
Set the Google API Key and Initialize Gemini 1.5 Pro
# Set the API Key
os.environ["GOOGLE_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass(prompt="GOOGLE_API_KEY")
# nitialize Gemini 1.5 Pro
llm = ChatGoogleGenerativeAI(model="gemini-1.5-pro", temperature=0)
Step 2: Defining the User Data Class
Next, we’ll create a UserDetails class to represent the user’s information. This class will use pydantic for data validation and provide optional fields for various user details.
# Data Model for User Details
class UserDetails(BaseModel):
language: Optional[str] = Field(
None, enum=["arabic", "english"],
description="The language preferred by the user."
)
first_name: Optional[str] = Field(
None,
description="The user's first name.",
)
last_name: Optional[str] = Field(
None,
description="The user's last name or surname.",
)
city: Optional[str] = Field(
None,
description="The city where the user resides.",
)
email: Optional[str] = Field(
None,
description="The user's email address.",
)
Step 3: Extracting User Details from Text
We’ll define a function to extract user details from a given input text. We’ll use the Gemini 1.5 Pro model through LangChain to create a chain that processes the input text and extracts the relevant details.
# Chain to Extract Details from Text
def extract_user_details(input_text: str) -> UserDetails:
parser = JsonOutputParser(pydantic_object=UserDetails)
extraction_prompt = PromptTemplate(
template="""Extract the following personal details from the text and provide them:
{input} \n \n {format_instructions}""",
input_variables=["input"],
partial_variables={"format_instructions": parser.get_format_instructions()},
)
chain = extraction_prompt | llm | parser
return chain.invoke(input_text)
Step 4: Updating and Merging User Details
We’ll create a function to update existing user details with new information. This function will merge the new details with the existing ones, ensuring that no data is overwritten unnecessarily.
# Update Existing Details with New Information
def merge_user_details(current_details: UserDetails, new_details: dict) -> UserDetails:
print("Data received:", new_details)
try:
personal_details = new_details
except KeyError as e:
print(f"KeyError: {e}. The key 'personaldetails' is not in the data dictionary.")
personal_details = {}
# Update only the empty fields in current_details
updated_details = {
'language': personal_details.get('language', current_details.language) if not current_details.language else current_details.language,
'first_name': personal_details.get('first_name', current_details.first_name) if not current_details.first_name else current_details.first_name,
'last_name': personal_details.get('last_name', current_details.last_name) if not current_details.last_name else current_details.last_name,
'city': personal_details.get('city', current_details.city) if not current_details.city else current_details.city,
'email': personal_details.get('email', current_details.email) if not current_details.email else current_details.email
}
return UserDetails(language=updated_details.get('language'),
first_name=updated_details.get('first_name'),
last_name=updated_details.get('last_name'),
city=updated_details.get('city'),
email=updated_details.get('email')
)
Step 5: Finding Missing Details
To ensure we collect all necessary information, we’ll create a function to find any missing details in the user’s information.
# Find Missing Details
def find_missing_details(user_details: UserDetails) -> List[str]:
empty_fields = []
for field in vars(user_details):
value = getattr(user_details, field)
if value in [None, "", 0]:
print(f"Field '{field}' is empty.")
empty_fields.append(field)
return empty_fields
Step 6: Prompting the User for Missing Information
We’ll create a function to prompt the user for any missing information in a conversational manner. This function will generate a prompt based on the missing fields and the user’s input.
# Prompt the User for Missing Information
def prompt_for_missing_info(missing_fields: List[str], user_input: str) -> str:
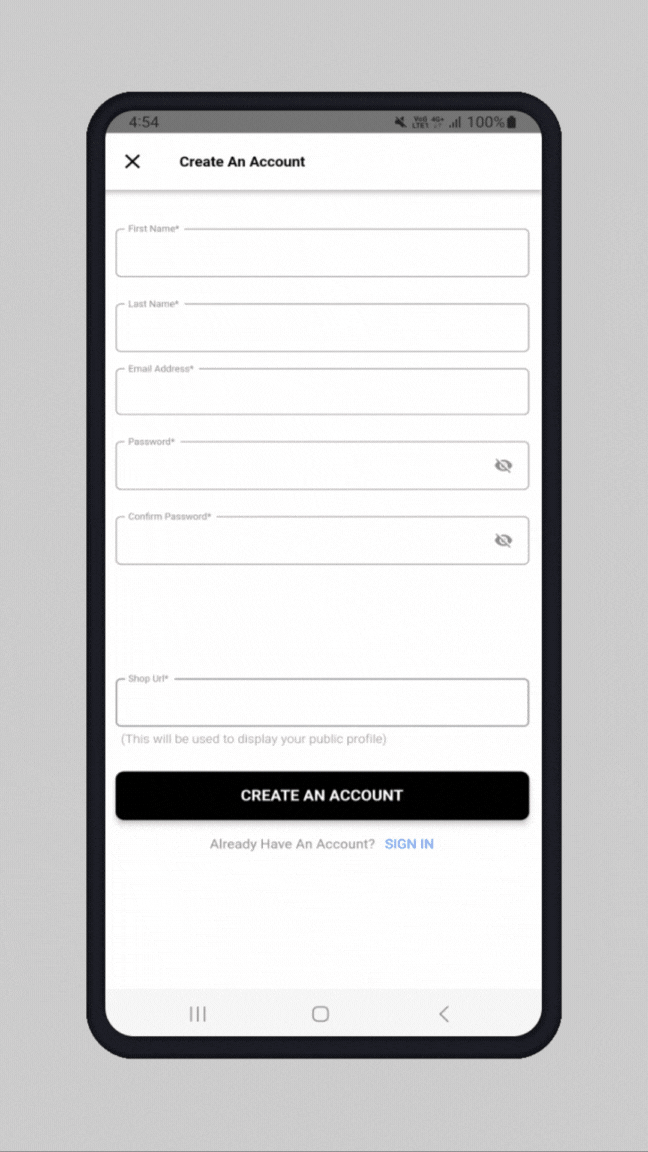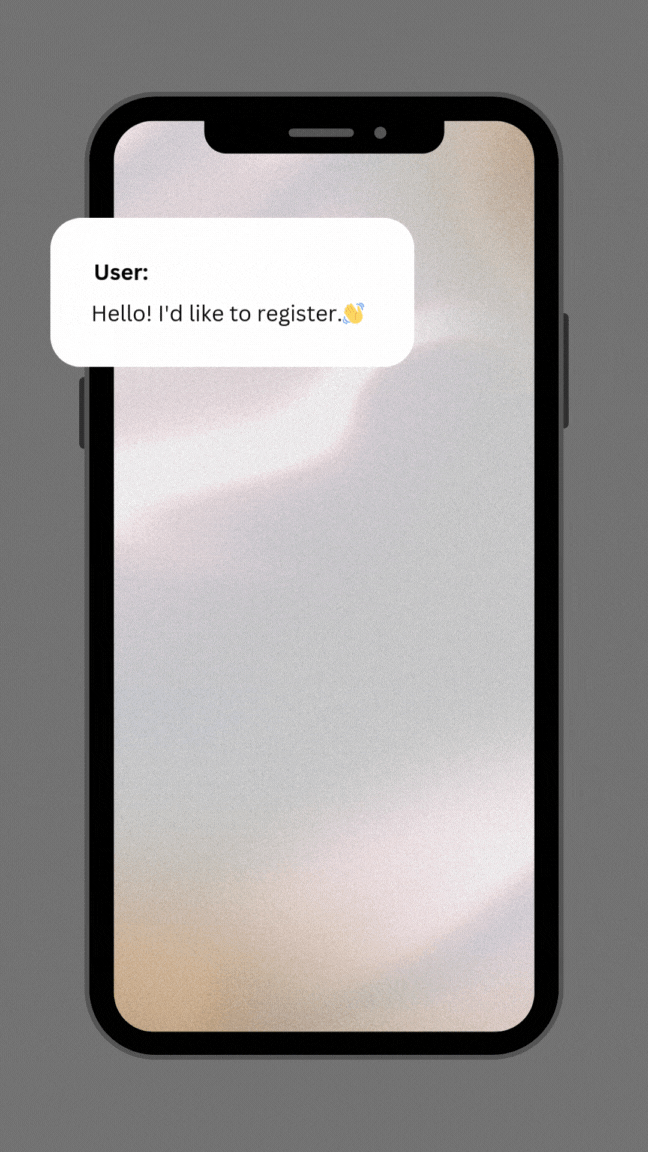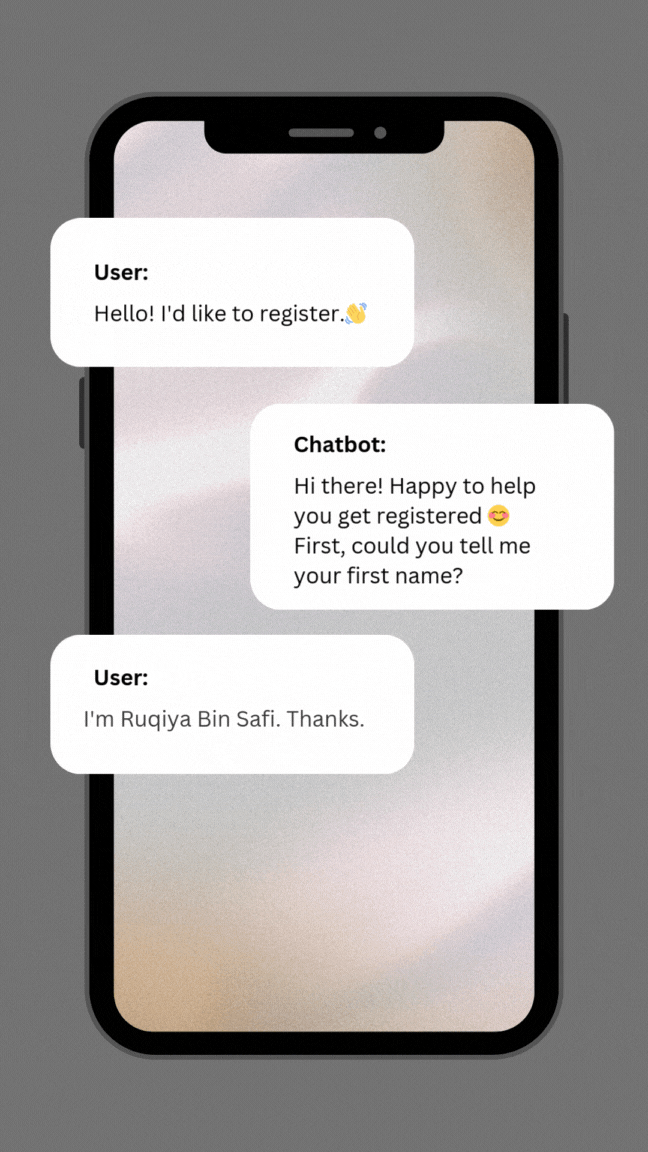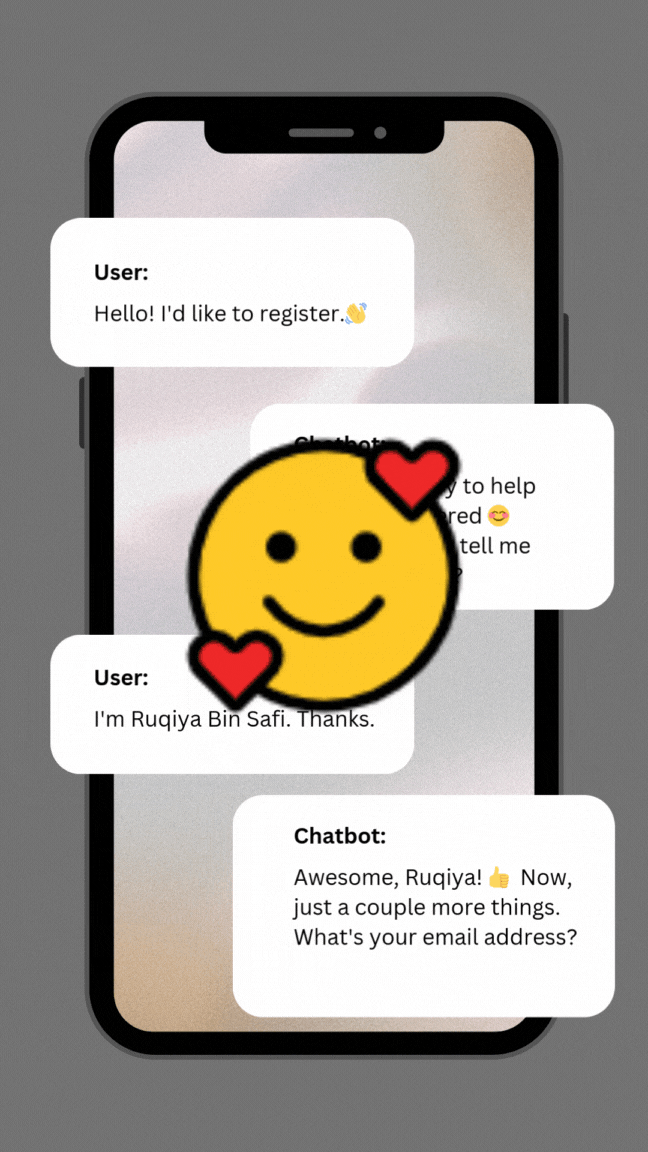
system_prompt = """You are a chatbot that collect user data that needs for registration. You talk to the user in a friendly way.
Interact with user message:
{user_input}
If use write arabic you must reply in Arbic. if use write english you must reply in English.
Here are some things to ask the user for in a conversational way:
### Missing fields list: {missing_fields}
Only ask one question at a time, even if you don't get all the info.
If there are four items in the list, say hello.
If there are less than four items and the list is not empty , make the conversation seem continuous.
If the list is empty, thank the user, tell them you've collected their registration data, and say goodbye.
"""
prompt = PromptTemplate(template=system_prompt, input_variables=['missing_fields', "user_input"])
chain = prompt | llm
ai_response = chain.invoke({"missing_fields": missing_fields, "user_input": user_input})
return ai_response.content
Step 7: Main Chatbot Function
We’ll initialize an empty UserDetails object and define the main function for our chatbot. This function will extract user details from the input text, merge them with the existing details, find any missing information, and prompt the user accordingly.
# Initialize an empty UserDetails object
current_user_details = UserDetails()
# The main chatbot function.
def chatbot_response(text_input: str) -> str:
global current_user_details
extracted_details = extract_user_details(text_input)
current_user_details = merge_user_details(current_user_details, extracted_details)
missing_fields = find_missing_details(current_user_details)
if not missing_fields:
messages = [
"Thank you, I've collected your data that we need for registration. See you soon!",
"Thanks! Your information has been recorded. Have a great day!",
"Data saved! You're all set. See you next time!",
"All done! Your registration is complete. See you soon!",
"Got it! Your data is safe with us. See you next time!"]
Thanks_message = random.choice(messages)
return Thanks_message
return prompt_for_missing_info(missing_fields, text_input)
# Before running the chat, check the data of the user that was just initialized.
print(current_user_details)
Step 8: Creating the Gradio Interface
Finally, we’ll use Gradio to create a user interface for our chatbot. This interface will allow users to interact with the chatbot and provide their information.
# Gradio Interface
chatbot = gr.Interface(
fn=chatbot_response,
inputs="text",
outputs="text",
live=False,
title="Chat to Collect and Save User Information",
description="Let's chat to register you for our services",
)
chatbot.launch(debug=True)
Step 9: Check If All Data Is Saved
# Check if all data of user is saved
print(current_user_details)
Wrap-Up:
By integrating Gemini 1.5 Pro into your applications, you can transform the way users interact with forms, making the process smoother and more enjoyable. This not only enhances user experience but also ensures more complete and accurate data collection. Embrace the power of conversational AI to take your form-filling processes to the next level.
While similar ideas exist, this solution is distinguished by its independence from specific functions, such as create_tagging_chain_pydantic from LangChain,which are tied to particular models like ChatGPT. Instead,it is designed to encompass Gemini 1.5 Pro/flash and all models as well.
Links:
Example of Applying the Idea in a Project:

 A journey of understanding, evaluating, and gaining deeper awareness of what truly makes a difference in the world of products.
A journey of understanding, evaluating, and gaining deeper awareness of what truly makes a difference in the world of products.